Volume 6 (2023) Issue 2 No.1 Pages 30-41
Abstract
Hematologic diseases frequently affect people >60 years old, and allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) is a potentially curative treatment for these patients. Although several multicenter studies proposed the risk assessment of allo-SCT for the elderly, they receive different treatments and management at each facility. Therefore, accumulating data from institutions that exhibit relatively the same treatment policy and patient care is important. This retrospective study aimed to clarify the prognostic factors of allo-SCT for the elderly in our institution. Of the 104 patients, 51.0% were 60-64 years old, and 49.0% were
Introduction
Hematologic diseases frequently affect people >60 years old1,2. For example, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), which is one of the major hematologic malignancies, and the median age of patients diagnosed with AML is 67 years3. Older hematologic disease patients were considered ineligible for allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) because of their frailties against treatment-related toxicities of allo-SCT4,5. In recent years, the development of reduced-intensity conditioning regimens, expanding donor availability including haplo-identical donors, and improvements in supportive care led to the extension of the age limit of allo-SCT to >70 years6. However, older patients are frail, and the outcomes of allo-SCT for older patients have not been satisfactory because of therapeutic toxicity or disease recurrence6,7. Therefore, deciding to strengthen the intensity of chemotherapies before allo-SCT to reduce the relapse risk of underlying disease following allo-SCT is difficult1,5,6,8. Although multiple institutions and organizations proposed various risk assessments and prognostic factors to improve allo-SCT outcomes in older patients1,5,8–10, each facility presents different treatment policies and care for older patients; thus, interpreting and comparing the results of previous studies from such multiple facilities is not easy5,9,10. While large-scale studies by multiple institutions are indispensable for improving allo-SCT outcomes in older patients, accumulating and analyzing data from institutions that present relatively the same treatment policy and patient care is also important. Therefore, this retrospective study aims to clarify the prognostic factors of allo-SCT for older hematologic disease patients in our institution.
Materials and Methods
Patients and clinical data
From January 2015 to December 2020, a cumulative total of 104 cases of allo-SCT were performed in Hamanomachi Hospital. A set of complete clinical data required in this study such as patients' age, patients' sex, body-mass index (BMI), performance status (PS), hematopoietic cell transplantation-specific comorbidity index (HCT-CI), primary disease, disease status prior to allo-SCT, donor source, HLA disparity, previous allo-SCT, donors' age, donors' sex, and presence of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) were available. The reduced-intensity conditioning was defined as a regimen with <8Gy total body irradiation,
Statistical analysis
The Fisher's exact test or the mxn Chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical variables and the Kruskal Wallis test was used for comparison of continuous variables. Survival was plotted using Kaplan-Meier curves, taking the interval from date of allo-SCT to death/relapse or last contact. Any patient who was alive at the last follow-up date was censored. Comparisons between each group were performed using the log-rank test. Relapse and treatment-related mortality were considered competing risk events and were analyzed using Fine & Gray's test. Univariate analysis was performed using logistic or exact logistic regression, and the parameters <0.05 were re-evaluated using multivariate analysis. Multivariate analysis was performed using logistic regression applying Firth's bias reduction. A p value<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using EZR12 and GraphPad Prism version 9 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California, USA).
Results
Patient characteristics
We identified 104 patients who received allo-SCT. The median age of the entire cohort was 64 (with a range of 60-74) years old. All patients received reduced-intensity conditioning regimens8. AML or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is the main indication for allo-SCT, followed by non-Hodgkin lymphoma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and other hematologic diseases. Moreover, 41 patients received related-peripheral blood, five received unrelated-peripheral blood, one received related-bone marrow, 18 received unrelated-bone marrow, and 39 received cord blood as the stem cell source. BMI of the patients ranged from 12.94-21.33 (with a median of 16.59), indicating that most patients (n=87, 83%) were underweight (BMI <18.5). With regards to the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG-PS), 48, 45, seven, and four patients had a score of 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Fifty-seven patients demonstrated a Karnofsky performance status (KPS) of
Survival, relapse, and treatment-related mortality
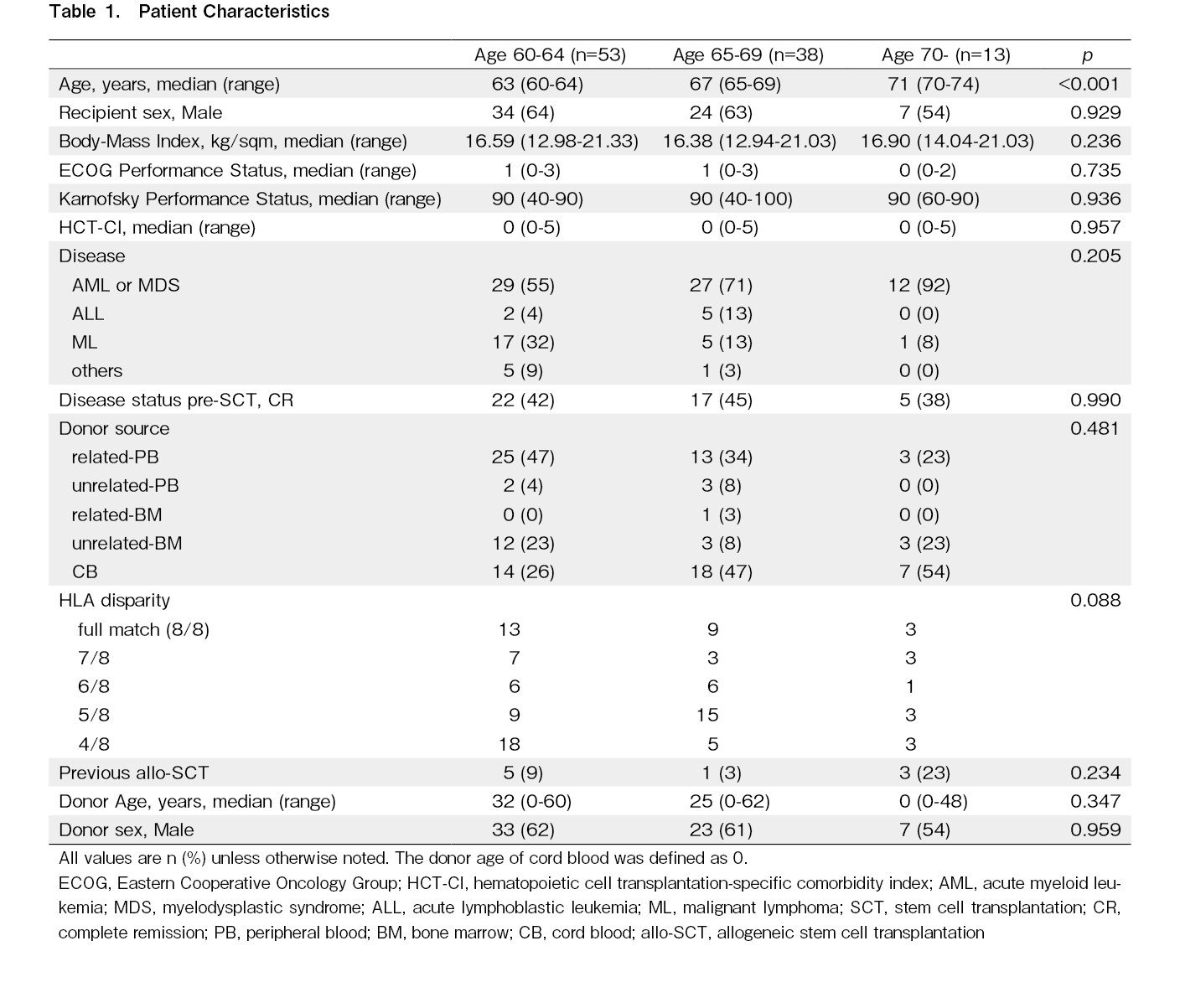
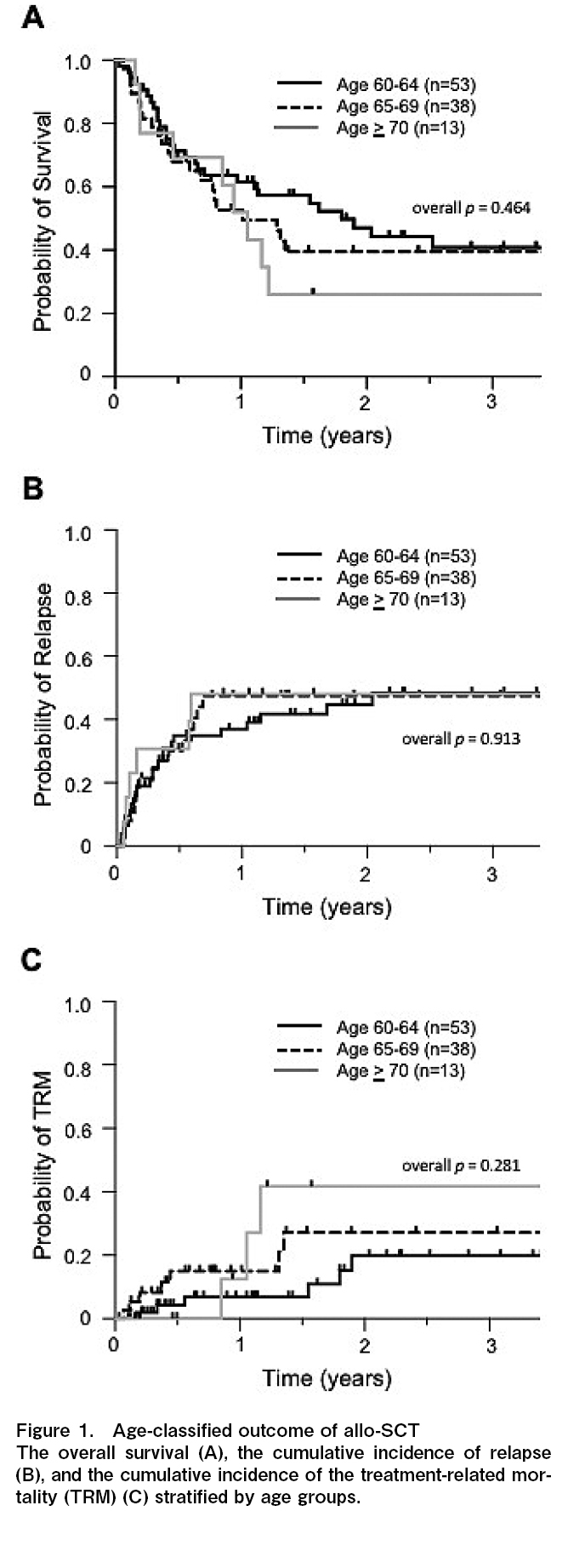
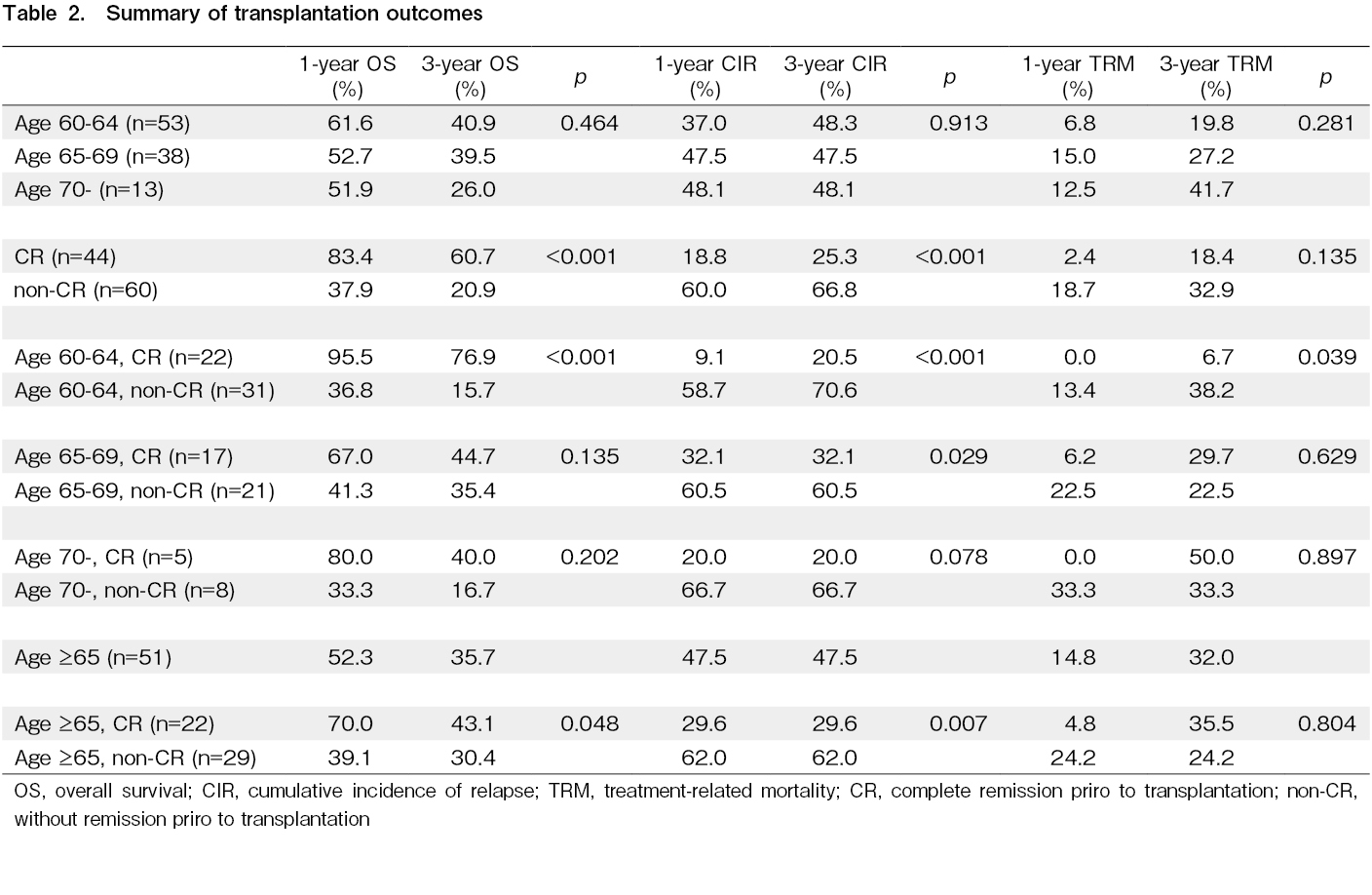
The 1-year overall survival (OS) was 61.6%, 52.7%, and 51.9%, and the 3-year OS was 40.9%, 39.5%, and 26.0% for patients 60-64, 65-69, and
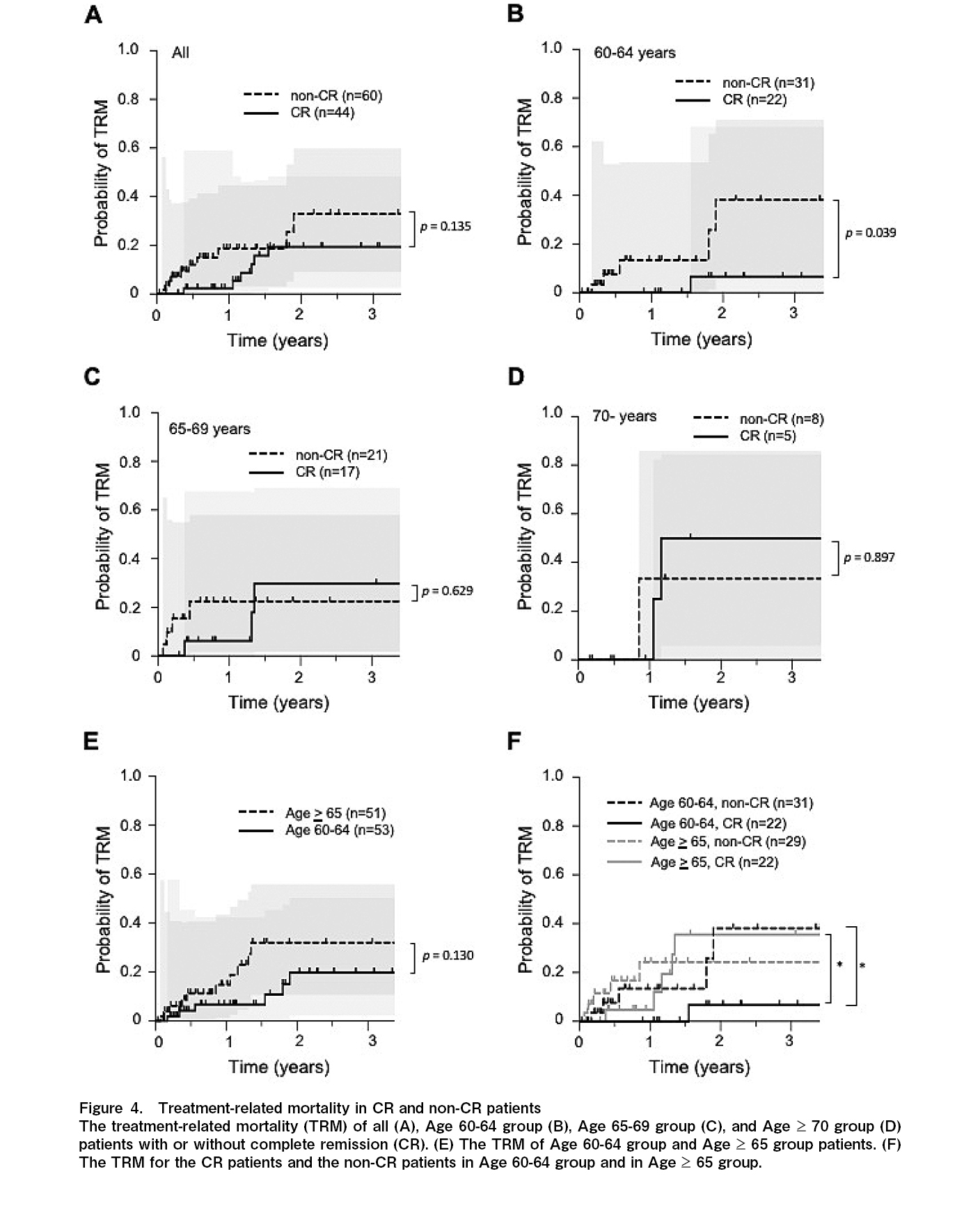
Because of frailty, the treatment-related mortality (TRM) is also a significant issue for older patients6,13,14. The 1-year cumulative incidence of TRM was 6.8%, 15.0%, and 12.5%, and the 3-year TRM was 19.8%, 27.2%, and 41.7% in patients 60-64, 65-69, and
Effect of disease control prior to allo-SCT on OS, relapse, and TRM
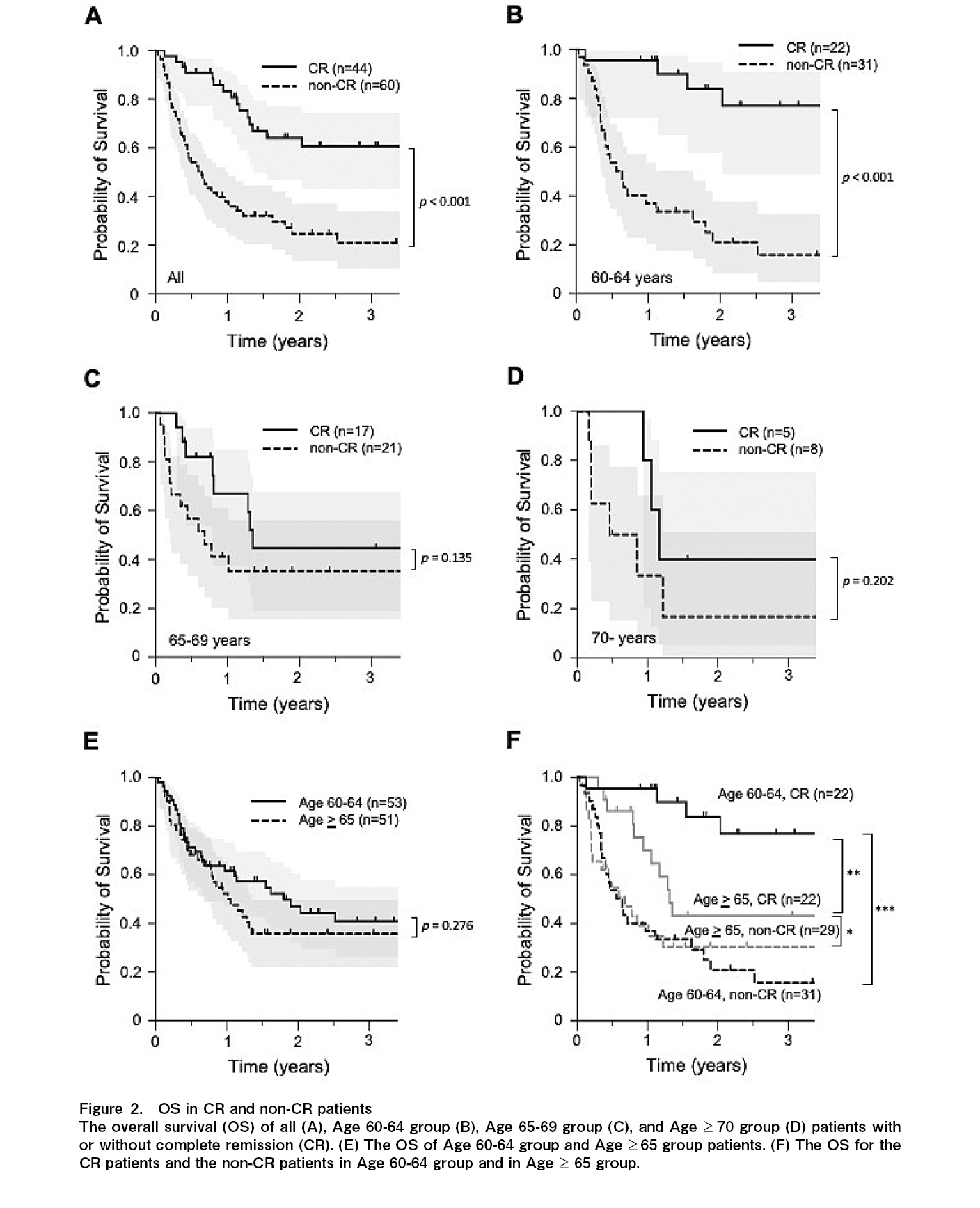
Previous studies reported that disease status prior to allo-SCT is one of the important factors for patients' survival following allo-SCT15–18. Therefore, we first evaluate the effect of disease status prior to allo-SCT on the survival of older patients. Overall, 44 (42.3%) patients achieved complete remission (CR) prior to allo-SCT, and 60 (57.7%) did not achieved CR (non-CR). The 1-year OS was 83.4% and 37.9%, and the 3-year OS was 60.7% and 20.9% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively. The median OS was not reached in the CR group, and it was 233 days (0.64 year) in the non-CR group (p<0.001) (Figure 2A and Table 2). Moreover, survival was evaluated based on age groups. For the 60-64 years old group (22 patients with CR and 31 patients without CR prior to allo-SCT), the 1-year OS was 95.5% and 36.8%, and the 3-year OS was 76.9% and 15.7% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively. The median OS was not reached in the CR group, and it was 233 days (0.64 year) in the non-CR group (p<0.001) (Figure 2B and Table 2). For the 65-69 years old group (17 patients with CR and 21 patients without CR prior to allo-SCT), the 1-year OS was 67.0% and 41.3%, and the 3-year OS was 44.7% and 35.4% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively. The median OS was 493 days (1.35 years) for the CR group and 248 days (0.68 year) for the non-CR group (p=0.135) (Figure 2C and Table 2). For the
Given that the disease status prior to allo-SCT significantly affected the 60-64 years old group, we combined the 65-69 years old and
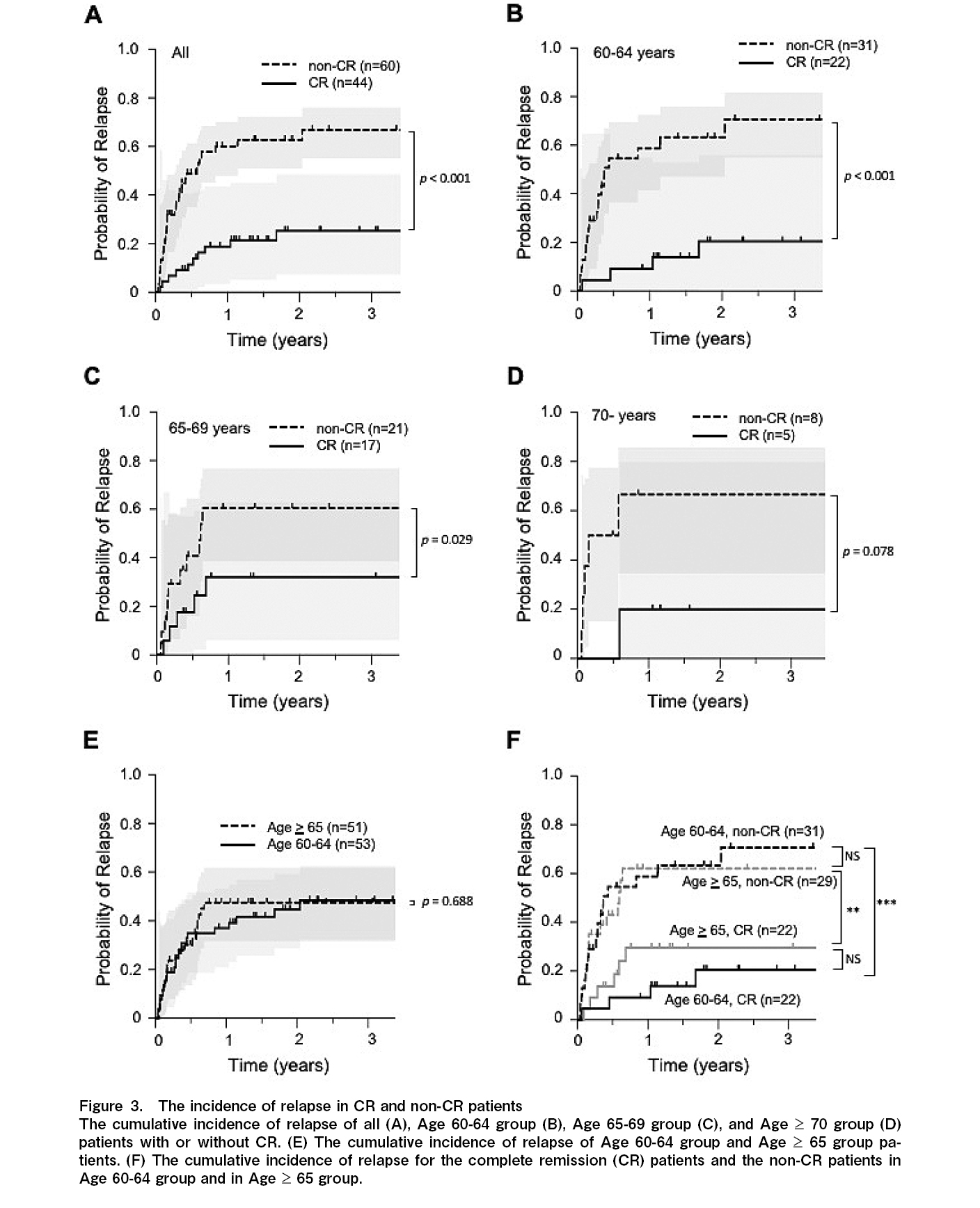
The 1-year CIR was 18.8% and 60.0%, and the 3-year CIR was 25.3% and 66.8% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively. The median relapse-free survival (RFS) was not reached in the CR group, and it was 210 days (0.58 year) in the non-CR group (p<0.001) (Figure 3A and Table 2). For the 60-64 years old group, the 1-year CIR was 9.1% and 58.7%, and the 3-year CIR was 20.5% and 70.6% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively. The median RFS was not reached in the CR group, and it was 134 days (0.37 year) in the non-CR group (p<0.001) (Figure 3B and Table 2). For the 65-69 years old group, the 1-year CIR was 32.1% and 60.5%, and the 3-year CIR was the same as those at one year for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively. The median RFS was not reached in the CR group, and it was 224 days (0.61 year) in the non-CR group (p=0.029) (Figure 3C and Table 2). For the
The 1-year cumulative incidence of TRM was 2.4% and 18.7%, and the 3-year TRM was 18.4% and 32.9% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively (p=0.135) (Figure 4A and Table 2). For the 60-64 years old group, the 1-year TRM was 0% and 13.4%, and the 3-year TRM was 6.7% and 38.2% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively (p=0.039) (Figure 4B and Table 2). For the 65-69 years old group, the 1-year TRM was 6.2% and 22.5%, and the 3-year TRM was 29.7% and 22.5% for the CR and non-CR groups, respectively (p=0.629) (Figure 4C and Table 2). For the
Risk and prognostic factors
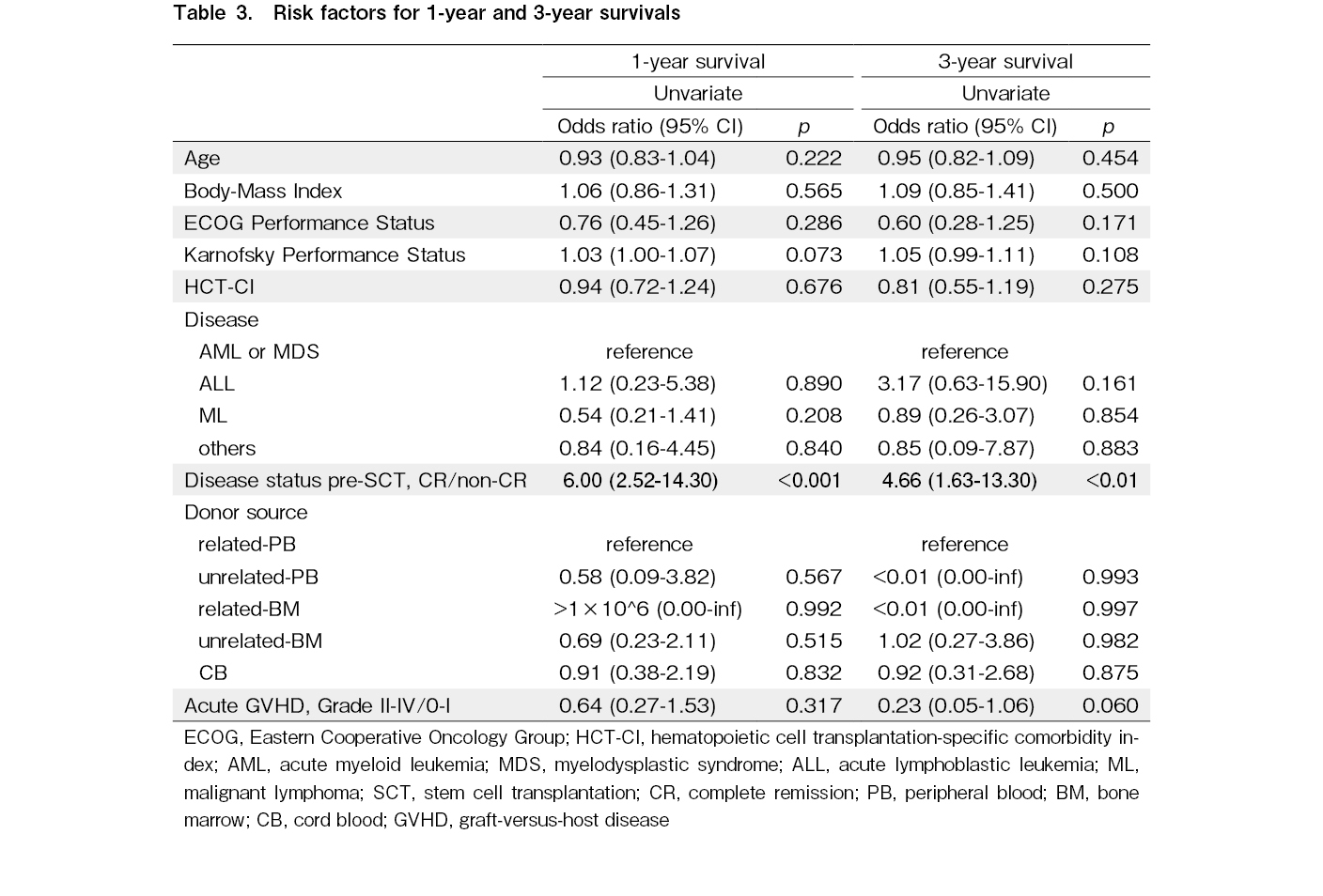
To reveal the survival risk factors in older patients following allo-SCT, we analyzed the relationship between OS and several factors including age, BMI, ECOG-PS, KPS, HCT-CI, underlying diseases, disease status prior to allo-SCT, donor source, and the presence of grade II-IV GVHD using univariate and multivariate analyses. These analyses were performed at one year and at three years, respectively. The disease status prior to allo-SCT is the only risk factor for OS both at one year (odds ratio (OR)=6.00, 95%CI 2.52-14.30, and p<0.001) and three years (OR=4.66, 95%CI 1.63-13.30, and p<0.01) (Table 3).
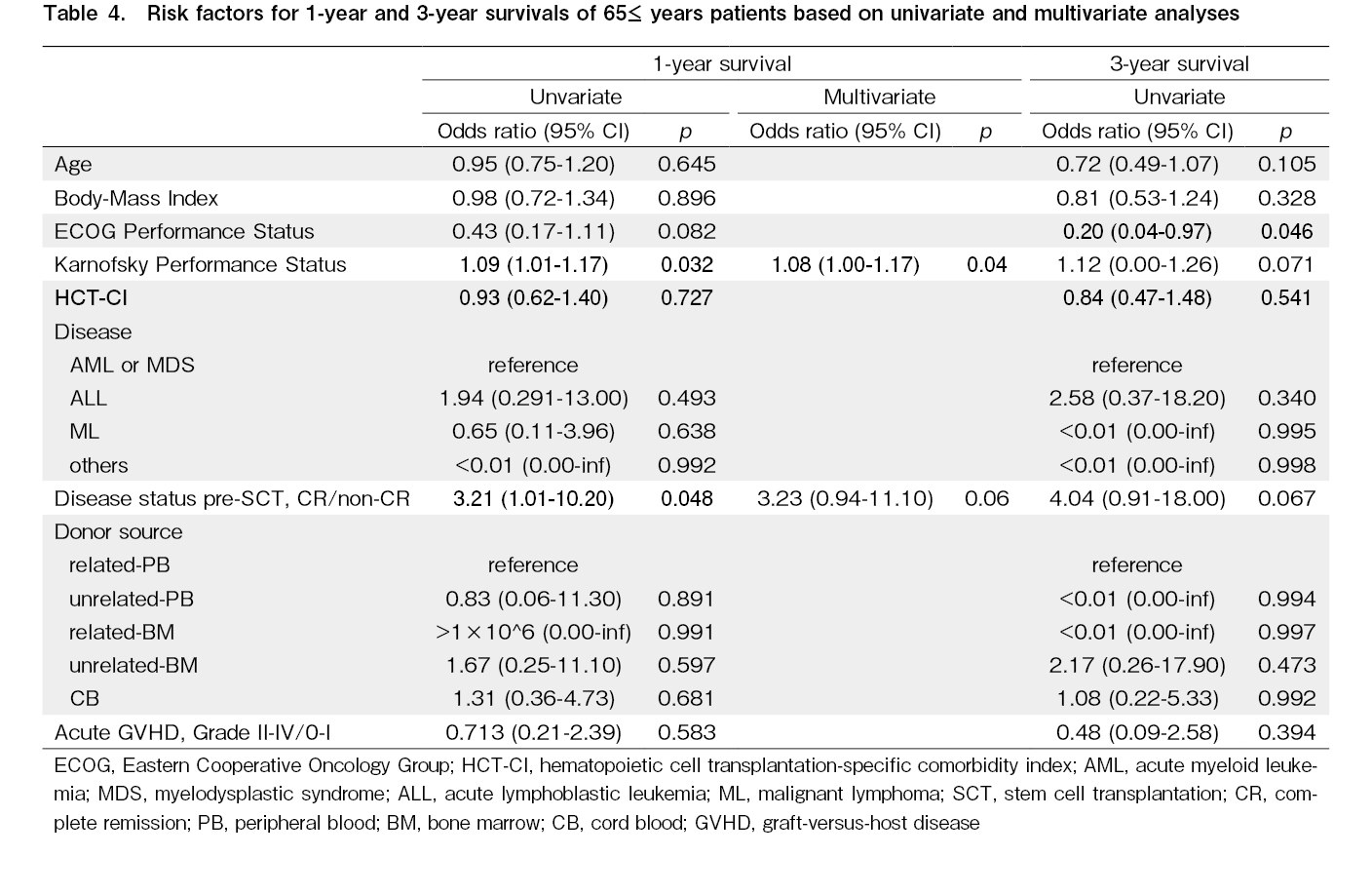
The same analyses were performed only for the
Discussion
While older patients were not considered to receive allo-SCT previously, recent advances in transplantation methods, supportive care, and donor availability allow older patients to receive allo-SCT4–6. However, given the fragility of older patients and the difficulty of care they need compared to younger patients, clarifying useful prognostic factors is necessary to improve the outcomes of allo-SCT in older patients. Some studies have focused on allo-SCT in older patients, and several potential prognostic factors have been suggested1,5,8–10; however, they have not been well investigated. Notably, large differences potentially exist among facilities regarding transplantation indications, treatment policies, and supportive care provision methods to older people; therefore, analyzing data at each facility that provides a relatively unified treatment and supportive care to older people is important5,9,10.
The 3-year OS, CIR, and TRM in our cohort were comparable with those reported in previous studies1,7,8, and no significant difference was found between each age group (Figure 1A-C). Generally, patients ≥60 years old are often regarded as the
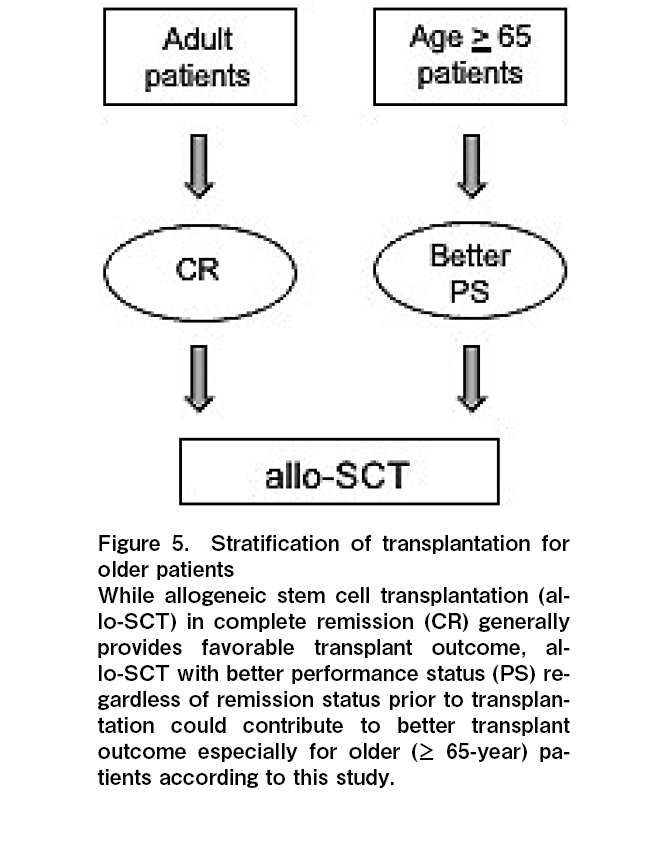
Importantly, it is very hard to clarify the cause of poor PS (both ECOG-PS and KPS) because underlying disease, disease status prior to allo-SCT, and co-morbidities are closely related to each other in allo-SCT24. Based on our data, there was no statistically significant relationship between PS and underlying disease, disease status prior to allo-SCT, and HCT-CI (data was not shown). Therefore, we assume PS could be one of the surrogate makers to comprehend the complicated status of older patients, and PS could be a useful indicator of better prognosis following allo-SCT for these patients.
Although the reason why KPS was the only risk factor for 1-year OS and ECOG-PS was the only risk factor for 3-year OS is not clear, the p values of ECOG-PS and KPS for survival were close to 0.05 (Table 4). This may indicate that much finer evaluation, such as using the KPS, could be more useful especially for early phases (1-year) of post-transplantation.
Moreover, in the future, chemotherapy-reduced/free treatment strategies that combine new agents (e.g., molecular-targeted drug25, bispecific CD19-directed
Notably, most patients (n=87, 83%) were underweight (BMI <18.5) compared to a previous study for Japanese people28. It is reported that normal weight (BMI 18.5-23.9) and underweight contributed to better OS compared to overweight (BMI >24.0)28. Our cohort had no patient that was overweight, suggesting that our data could be potentially biased.
Despite the small sample size, and retrospective single-institutional experiences, our study suggests that PS before transplantation could be a useful prognostic factor for older patients. Therefore, PS might be one of the useful indicators for patients to make a decision on allo-SCT, especially for older patients. Therefore, we try to introduce exercise a tolerance test prior to allo-SCT to evaluate patients' activity in our institution. And we also try to introduce physical exercise for patients prior to allo-SCT to improve PS and the outcome of transplantation. Our findings should be confirmed by future prospective studies in a larger group of patients.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all medical staff working in Hamanomachi Hospital.
Author Contributions
Contribution: T. Shima coordinated the project, performed the allo-SCT, designed and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript; K.T., S.U., T.Y., M.M.,
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available on the website.
References
1.Hsu J, Chen Z, Shore T, Gergis U, Mayer S, Phillips A, et al. Outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplant for elderly patients with hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020; 26: 789-97.
2.Bron D, Ades L, Fulop T, Goede V, Stauder R; Elderly Task Force in Hematology EHA SWG. Aging and blood disorders: new perspectives, new challenges. Haematologica. 2015; 100: 415-7.
3.Estey EH. Acute myeloid leukemia: 2013 update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2013; 88: 318-27.
4.Podoltsev NA, Stahl M, Zeidan AM, Gore SD. Selecting initial treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia in older adults. Blood Rev. 2017; 31: 43-62.
5.Duarte RF, Sánchez-Ortega I. HSCT in elderly patients. The EBMT Handbook-Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies, 7th edition. 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553964/
6.Lipof JJ, Loh KP, O'Dwyer K, Liesveld JL. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for older adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers (Basel). 2018; 10: 179.
7.Muffly L, Pasquini MC, Martens M, Brazauskas R, Zhu X, Adekola K, et al. Increasing use of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients aged 70 years and older in the United States. Blood. 2017; 130: 1156-64.
8.Aoki J, Kanamori H, Tanaka M, Yamasaki S, Fukuda T, Ogawa H, et al. Impact of age on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced intensity conditioning in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2016; 91: 302-7.
9.Basak GW, Sánchez-Ortega I, Beohou E, van der Werf S, Labopin M, van Biezen A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in elderly patients aged 65 and older: A Retrospective Analysis By the Complications and Quality of Life Working Party of the EBMT. Blood. 2016; 128: 681.
10.Rashidi A, Ebadi M, Colditz GA, DiPersio JF. Outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22: 651-7.
11.Giralt S, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Bacigalupo A, Horowitz M, Pasquini M, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen workshop: defining the dose spectrum. Report of a workshop convened by the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009; 15: 367-9.
12.Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013; 48: 452-8.
13.Hahn T, McCarthy PL Jr, Hassebroek A, Bredeson C, Gajewski JL, Hale GA, et al. Significant improvement in survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation during a period of significantly increased use, older recipient age, and use of unrelated donors. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31: 2437-49.
14.Zhao Y, Song Y, Yang F, Li F, Yang D, Wu T. Better outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning in elderly patients with hematological malignancies. Blood. 2021; 138 (Suppl 1): 4864.
15.Armand P, Gibson CJ, Cutler C, Ho VT, Koreth J, Alyea EP, et al. A disease risk index for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012; 120: 905-13.
16.Murdock HM, Kim HT, Denlinger N, Vachhani P, Hambley B, Manning BS, et al. Impact of diagnostic genetics on remission MRD and transplantation outcomes in older patients with AML. Blood. 2022; 139: 3546-57.
17.Moukalled NM, Kharfan-Dabaja MA. What is the role of a second allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia?. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020; 55: 325-31.
18.Sorror ML, Appelbaum FR. Risk assessment before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for older adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 2013; 6: 547-62.
19.Lazarevic VL. Acute myeloid leukaemia in patients we judge as being older and/or unfit. J Intern Med. 2021; 290: 279-93.
20.Singh S, Bajorek B. Defining ‘elderly’ in clinical practice guidelines for pharmacotherapy. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2014; 12: 489.
21.Ravanat JL, Remaud G, Cadet J. Measurement of the main photooxidation products of 2'-deoxyguanosine using chromatographic methods coupled to mass spectrometry. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000; 374: 118-27.
22.Grochow LB. Parenteral busulfan: Is therapeutic monitoring still warranted?. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002; 8: 465-7.
23.De Lima M, Couriel D, Thall PF, Wang X, Madden T, Jones R, et al. Once-daily intravenous busulfan and fludarabine: clinical and pharmacokinetic results of a myeloablative, reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and MDS. Blood. 2004; 104: 857-64.
24.Penack O, Peczynski C, Mohty M, Yakoub-Agha I, de la Camara R, Glass B, et al. Association of pre-existing comorbidities with outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. A retrospective analysis from the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022; 57: 183-90.
25.Chi SG, Minami Y. Emerging targeted therapy for specific genomic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23: 2362.
26.Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gökbuget N, Fielding AK, Schuh AC, Ribera JM, et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376: 836-47.
27.Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, Rives S, Boyer M, Bittencourt H, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378: 439-48.
28.Yu J, Lin S, Luo Y, Shi J, Tan Y, Lai X, et al. Obesity is correlated with poor outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute leukemia. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020; 50: 889-96.
Search
News